The purpose of this post is to help you understand the fundamentals of SAS programming. It is intended to give first time users an idea about the SAS software and how to access it and get you up and ready with SAS programming. At the end of this tutorial, you would be acquainted with SAS basic syntax rules, how to enter data into SAS, variable types and how to run a program in SAS.
If you really want to make your career in analytics, you should focus on learning SAS programming as SAS is a world leader in softwares for advanced analytics. To see the real potential of SAS programming, login to any job portal and search for jobs required skill set of SAS. You would find a large number of jobs waiting for you if you know SAS.
SAS stands for Statistical Analysis System.
SAS can perform the following tasks:
- It allows you to enter, retrieve and manage your data easily
- It can read data from various external sources (Excel, CSV, Text files, Databases, Webpage etc)
- You can explore and manipulate data in SAS.
- It can analyze your data statistically and mathematically. Includes various statistical techniques.
- It can generate beautiful graphs and tables.
- You can run SQL queries on SAS datasets.
- You can automate repetitive tasks with SAS Macros.
- It can develop entirely new software applications.
Free Download and Install SAS Software
To access and learn SAS for free, check out this link - Free Access to SAS Software
Basics of SAS Programming
SAS has three main windows :
- Editor Window: where you type programs for analyzing data
- Log Window: where error messages and executed SAS commands are printed
- Result Window: where the result of SAS programs are printed.
Basic SAS Program
Let's look at a simple SAS program :
 |
| A Simple SAS Program |
data example1; input name $ ID; cards; Sam 12 Sandy 13 Reno 11 Farhan 10 ; proc print; run;
data example1;: This line initiates a data step and creates a new dataset named "example1" to store the data.input name $ ID;: This line defines the variables for the dataset. It specifies that there are two variables: "name" and "ID." The dollar sign ($) after "name" indicates that it is a character variable, and the lack of a dollar sign after "ID" indicates that it is a numeric variable.cards;: This keyword signals the start of inline data. The data enclosed betweencards;and the next semicolon (;) will be read as input data for the dataset.- The lines following
cards;contain the actual data values. Each line represents one observation (row) in the dataset. In this example, there are four observations with two variables each: "name" and "ID." proc print;: This line initiates theproc printprocedure, which is used to display the contents of a dataset.run;: This line signifies the end of the data step and the end of theproc printprocedure.
When you run this SAS code, it will create the dataset "example1" with the given data and then print its contents to the results window. The output will show the "name" and "ID" values for each observation in the dataset.
How to Submit SAS Program
To submit the SAS program, press F3 shortcut key. Alternatively, you can click on click on the icon of "the little guy running" at the top of the SAS tool bar.
SAS Log Window
It is where error messages and executed SAS commands are printed.
 |
| SAS Log Window |
SAS Results Window
 |
| SAS Output Window |
SAS Libraries
SAS files are stored in a SAS library. A SAS library is simply a collection of SAS files (data sets) that are stored in a folder. SAS files are stored either temporarily or permanently. By default, it is stored in a temporary library called Work.
1. Temporary : When you don't specify a library name at all, then the file is stored in a temporary SAS library called Work. When you close out the SAS session in which you created the SAS file, the temporary library and all of its files are removed from your computer's memory.
data example;
In this case, example is a data set that is stored in Work library. Note : You can specify the library name Work followed by dot (.) and then data set name.
data work.example;
2. Permanent : If you use a library name other than the default library name 'Work' when creating a SAS file, then the file is stored permanently until you delete it. That is, you can use permanent SAS libraries and their contents in subsequent SAS sessions.
You can specify the library name followed by dot (.) sign and then data set name.
data mydata.example;In this case, example1 is a data set that is stored in mydata library.
How to Upload and Import a File into SAS Studio
Please follow the steps shown in the video below to upload and import a file into SAS Studio.
- To import a file into SAS Studio, begin by navigating to the desired folder where you want to import the file. You can find the folder on the left-hand side of the screen under the
Server Files and Folderspane. - Next, right-click on the folder and choose the
Upload Filesoption. - Click on the
Choose Filesbutton and select the CSV file you wish to import. Then, click theUploadbutton to start the upload process. - Once the file is uploaded, find it in the folder where it was imported. Right-click on the file and choose the
Import Dataoption. - Click on the
Runbutton to start the import process. - SAS Studio will then import the CSV file and create a new dataset. By default, the imported dataset will be available in the WORK library.
SAS Programming Rules
When it comes to programming in SAS, there are several best practices and rules that can help improve code readability, efficiency, and maintainability. Here are some important SAS programming rules to keep in mind:
I. Rules for SAS statements
- All SAS statements (except those containing data) must end with a semicolon (;).
Example : "DATA example1;" is an example of a SAS statement.
- Any number of SAS statements can appear on a single line provided they are separated by a semicolon.
Example : "DATA example1; Input Name $ ID;" is an example of a SAS statement.
- SAS statements typically begin with a SAS keyword. (DATA, PROC)
- SAS statements are not case sensitive, that is, they can be entered in lowercase, uppercase, or a mixture of the two.
Example : SAS keywords (DATA, PROC) are not case sensitive
- A delimited comment begins with a forward slash-asterisk (/*) and ends with an asterisk-forward slash (*/). All text within the delimiters is ignored by SAS.
II. Rules for SAS names
- All names must contain between 1 and 32 characters.
- The first character appearing in a name must be a letter (A, B, ...Z, a, b, ... z) or an underscore (_). Subsequent characters must be letters, numbers, or underscores. That is, no other characters, such as $, %, or & are permitted. Blanks also cannot appear in SAS names.
- SAS names are not case sensitive, that is, they can be entered in lowercase, uppercase, or a mixture of the two. (SAS is only case sensitive within quotation marks.)
III. Rules for SAS variables
If the variable in the INPUT statement is followed by a dollar sign ($), SAS assumes this is a character variable. Otherwise, the variable is considered as a numeric variable.
Difference between PROC and DATA Step
DATA STEPAny portion of a SAS program that begins with a DATA statement and ends with a RUN statement is called a DATA Step.
DATA steps are used to manage data. In detail, DATA steps are used to read raw or external data into a SAS data set, to modify data values, and to subset or merge data sets.
Any portion of a SAS program that begins with a PROC statement and ends with a RUN statement is called a PROC Step or Procedures.
PROC steps are in-built programs that allow us to analyze the data contained in a SAS data set. PROC steps are used to calculate descriptive statistics, to generate summary reports, and to create summary graphs and charts.
data temp; input ID Company $20.; cards; 12 Reliance 13 Google 11 Microsoft 10 SAS 9 Tom 10 SAP ; proc print; run;
The above program creates a dataset named temp which is stored in WORK library. In the dataset, there are 2 variables/columns - Company and ID which contains 6 observations/rows. The command PROC PRINT tells SAS to print the dataset in Results Window.
How to Filter Data in SAS
The IF statement is used to apply a condition to filter the data.
data out; set temp; if ID > 10; run;
The SET statement allows you to read values from a SAS data set (temp). The SAS Statement 'IF ID > 10' tells SAS to read only those ID values that are greater than 10. Later SAS paste these values into a new data set (OUT) without overwriting existing data set (temp)
Multiple Conditions - The following SAS code is using the multiple conditions in the IF statement.
data out; set temp; if ID = 10 and Company = 'SAS'; run;
if ID = 10 and Company = 'SAS';: In this case, IF statement selects records where both the "ID" variable is equal to 10 and the "Company" variable is equal to 'SAS'.
IF-THEN-ELSE Statements
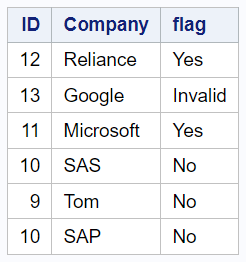
The following code creates a new "flag" variable where the value 'No' is assigned when the "ID" is less than or equal to 10, 'Yes' when the "ID" is greater than 10 and less than or equal to 12, and 'Invalid' for any other value of "ID" greater than 12, based on the values in the existing dataset "temp". The "flag" variable is a character variable with a length of 8 characters.
data out; set temp; length flag $8; if ID <=10 then flag='No'; else if ID > 10 and ID <=12 then flag='Yes'; else flag='Invalid'; run;
How to Sort Data in SAS
In SAS, the PROC SORT procedure sorts a dataset.
proc sort data=temp; by ID; run;
by ID;: This line specifies the variable "ID" that will be used for sorting the dataset. When you sort the data, the values of the "ID" variable will be arranged in ascending order by default.
To sort the dataset in descending order, you can use the keyword descending after BY statement.
proc sort data=temp; by descending ID; run;
How to Calculate Summary in SAS
In SAS, PROC MEANS is used to calculate summary statistics, such as count, mean, minimum, maximum, standard deviation and more for one or more variables in a SAS dataset. The following code calculates descriptive statistics for the variable "ID" in the dataset "temp."
proc means data=temp; var ID; run;
How to Generate Frequency Distribution in SAS
PROC FREQ is a SAS procedure used to generate frequency tables, which display the distribution of values within categorical variables.
The following code shows how to use PROC FREQ with the built-in SAS dataset "sashelp.cars". We have created a new dataset named "cars" by copying the content of the built-in dataset "sashelp.cars".
/* Step 1: Access the sashelp.cars dataset */ data cars; set sashelp.cars; run; /* Step 2: Use PROC FREQ to analyze the "make" variable */ proc freq data=cars; tables make; run;
Within the PROC FREQ step, the "tables" statement is used to specify the variable "make" for which we want to calculate the frequency table. In this case, we are interested in analyzing the distribution of the "make" variable, which represents the car manufacturer.
How to Combine Datasets in SAS
PROC APPEND is a SAS procedure used to combine or append datasets. It is commonly used when you have multiple datasets with the same structure (same variables and data types) and you want to merge them vertically, concatenating one dataset below the other.
/* Create dataset1 */ data dataset1; input ID Name $ Age Grade $; cards; 1 John 18 A 2 Jane 17 B 3 Alex 19 A ; run; /* Create dataset2 */ data dataset2; input ID Name $ Age Grade $; cards; 4 Sarah 16 B 5 Mike 18 C 6 Emily 17 A ; run; /* Use PROC APPEND to combine datasets */ proc append base=dataset1 data=dataset2; run;
After combining the datasets, Dataset1 now has 6 observations. It originally had 3 observations. Please refer to the log below.
NOTE: Appending WORK.DATASET2 to WORK.DATASET1. NOTE: There were 3 observations read from the data set WORK.DATASET2. NOTE: 3 observations added. NOTE: The data set WORK.DATASET1 has 6 observations and 4 variables.







Hi.. I was seraching for a free SAS book online and found this website. its excellent.. keep u the great work
ReplyDeletethanks
It is great site for SAS Learners. Appreciate your great work.
ReplyDeletethanks
awesome site to learn sas, nd thanx a lot ..
ReplyDeleteThis is the wonderful job you're doing. Thanks.
ReplyDeleteAwesome site to learn SAS and data analysis.
ReplyDeleteExcellent work! Just started as a student (programmer) assistent, and is learning SAS. This site is helping alot!
ReplyDeleteGreat work..Really very useful for people who wants to start SAS from ground level.Everyone can easily understand the subject.
ReplyDeleteExcellent work sir.... Thank you very much
ReplyDeleteexcellent website to revisit the concepts for SAS and sql. Keep up the good work !!!
ReplyDeleteU have made learning so easy with Examples. Thanks a Ton!..keep up the good work to help others!.. :)
ReplyDeleteBeginners delight! Keep posting...
ReplyDeleteexcellent work sir thanks...........
ReplyDeleteSuch a great stuff from such a great person!! Thank you :)
ReplyDeleteTHANK YOU VERY MUCH I GOT UR SITE INFO FROM AON EMPLOYEE
ReplyDeleteThank you for stopping by my blog. Say 'Thanks' to the Aon Employee who spreaded the word about 'ListenData' :D
Deleteno more words really very nice..why don't you take a classes?
ReplyDeleteThank you :)
Thank you for stopping by my blog. I'll think about taking classes :)
DeleteThank you sir.. :)
ReplyDeleteThx for sharing it's very easy to use
ReplyDeleteHi, I am a new learner of SAS. I had lot of apprehension about SAS because I thought programming is not my cup of tea. I found this website and really enjoying learning SAS. Thanks a ton for sharing your knowledge in such a clear way. Keep up good work. look forward to many more tutorial sessions...
ReplyDeleteThank you very much for taking time out of your busy schedule to give your feedback. Cheers!
DeleteHi, Deepanshu, thanks for the outstanding explanation. Iam a beginner in SAS CLINICAL. What's your suggestions for a beginner like me with out any prior programming language. Your kind suggestions will be appreciated. Thanks. Azhar.
Deleteexcellent website for beginners . Thank you so much for such an amazing content.
ReplyDeleteguys sasstudio is not accepting input from my keyborad please suggest what should i do
ReplyDeleteGREAT WORK, THANK YOU SO MUCH :)
ReplyDeleteGreat work Sir.
ReplyDeleteVery useful. thank you
ReplyDeleteIt's an wonderful platform for beginners especially without programming language
ReplyDeleteThank you very much!! This is really helpful.
ReplyDeleteReally good . and thank you so much for this fantastic content.
ReplyDeleteSo easy to learn.the way you described is great.
ReplyDeleteExcellent work done by developers....very easy way to learn SAS through this content.....fantastic content and easy to understand
ReplyDeleteBest place to refresh SAS. Great job. Awesome, I'm liking it a lot.
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it useful. Cheers!
ReplyDeletegood deeds...
ReplyDelete