This tutorial explains how to use the INTERSECT operator in PROC SQL in SAS, along with examples.
In PROC SQL, the INTERSECT operator is used to find the common records that exist in tables. The basic syntax of INTERSECT OPERATOR within PROC SQL is as follows :
PROC SQL; SELECT * FROM dataset1 INTERSECT SELECT * FROM dataset2; QUIT;
Creating Sample Datasets
The following programs creates two sample SAS datasets that will be used to explain examples in this tutorial.
data dataset1; input ID Name $; datalines; 1 Dave 2 Mario 3 Steve ; run; data dataset2; input ID Name $; datalines; 1 Dave 2 Steve 4 Priya ; run;

In this case, it stores the common records of both tables into a new dataset named 'outdata'.
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE outdata as SELECT * FROM dataset1 INTERSECT SELECT * FROM dataset2; QUIT;

It returned only one row as it was the only matching rows in both datasets.
Finding Common Records Based on Specific Columns
In this example, we are finding common records based on a column named "Name".
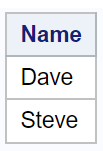
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE outdata as SELECT Name FROM dataset1 INTERSECT SELECT Name FROM dataset2; QUIT;
It returned two rows as 'Dave' and 'Steve' are common names in both tables but they have different IDs.


Share Share Tweet