This tutorial is designed for beginners who want to get started with PROC SQL. It also includes a detailed comparison of the functions used in SAS and PROC SQL.
Syntax of PROC SQL
The syntax of PROC SQL is as follows:
PROC SQL; SELECT column(s) FROM table(s) | view(s) WHERE expression GROUP BY column(s) HAVING expression ORDER BY column(s); QUIT;
The SQL statements must be specified in the following order:
- SELECT : Specify the columns (variables) to be selected.
- FROM : Specify the table (dataset) to be queried.
- WHERE : Filters the data based on a condition.
- GROUP BY : Classifies data into groups based on the specified columns.
- HAVING : Filters data with the GROUP BY clause.
- ORDER BY : Sorts the rows (observations) by the specified columns.
Note : SELECT FROM clauses are required. All the other clauses are optional.
PROC SQL statement calls the SQL procedure and QUIT statement ends the procedure.
To memorize the order of SQL queries, you can use the mnemonic "SFWGHO".
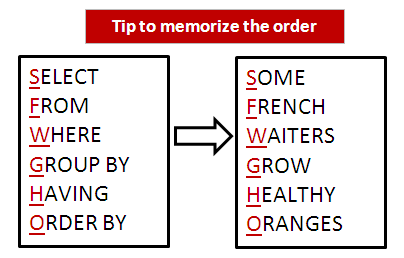
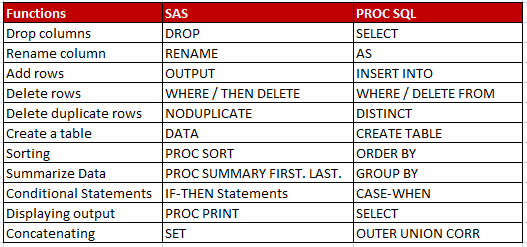
We are going to look at the difference between SAS and PROC SQL.
| SAS | SQL |
|---|---|
| Dataset | Table |
| Observation | Row |
| Variable | Column |
| Functions | SAS | PROC SQL |
|---|---|---|
| Select/Drop columns | KEEP / DROP | SELECT |
| Rename column | RENAME | AS |
| Add rows | OUTPUT | INSERT INTO |
| Delete rows | WHERE/THEN DELETE | WHERE / DELETE FROM |
| Delete duplicate rows | NODUPLICATE | DISTINCT |
| Create a table | DATA | CREATE TABLE |
| Sorting | PROC SORT | ORDER BY |
| Summarize Data | PROC SUMMARY, FIRST. LAST. | GROUP BY |
| Conditional Statements | IF-THEN Statements | CASE-WHEN |
| Displaying output | PROC PRINT | SELECT |
| Concatenating | SET | OUTER UNION CORR |
You would hear the word 'schema' from SQL programmers. It refers to design of database. In other words, it is the framework of database.
In the SAS program below, we are creating sample data for illustration purposes by extracting a few observations from the dataset "BWEIGHT" stored in the SASHELP library.
data outdata ; set SASHELP.BWEIGHT (obs=1000); run;
PROC SQL STATEMENTS
proc sql; select * from outdata; Quit;
Asterisk (*) is used to select all columns (variables) in the order in which they are stored in the table. Outdata is the table (dataset) from which we need to select the columns.
To display the list of columns to the SAS log, use FEEDBACK option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql feedback; select * from outdata; Quit;
The SAS log is shown below:
71 proc sql feedback;
72 select *
73 from outdata;
NOTE: Statement transforms to:
select OUTDATA.Weight, OUTDATA.Black, OUTDATA.Married, OUTDATA.Boy, OUTDATA.MomAge, OUTDATA.MomSmoke, OUTDATA.CigsPerDay,
OUTDATA.MomWtGain, OUTDATA.Visit, OUTDATA.MomEdLevel
from outdata;
74 Quit;
In the SELECT clause, multiple columns are separated by commas.
proc sql; select weight,married from outdata; Quit;
In the SELECT clause, Weight and Married columns are specified so that we can select them from OUTDATA table.
Suppose you want to limit the number of rows that PROC SQL displays, use the OUTOBS= option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql outobs=50; select weight,married from outdata; Quit;
Suppose you want to rename a variable, use the column alias AS option in the PROC SQL statement.
options nolabel; proc sql; select weight,married as marriage from outdata; Quit;
The variable name has been renamed from married to marriage. options nolabel tells SAS not to use variable labels in SAS procedures. I used it so that you can see variable name has been changed to marriage.
Suppose you want to create a new variable that contains calculation.
proc sql; select weight, (weight*0.5) as newweight from outdata; Quit;
A new variable has been created and named newweight which is calculated on the basis of the existing variable weight.
The keyword CALCULATED is used to refer a previously calculated variable.
proc sql; select weight, (weight*0.5) as newweight, CALCULATED newweight*0.25 as revweight from outdata; Quit;
The keyword DISTINCT is used to eliminate duplicate rows from your query results.
In the following program, we are asking SAS to remove all those cases where in duplicates exist on combination of both the variables - weight and married.
proc sql; select DISTINCT weight, married from outdata; quit;
The DISTINCT * implies cases having same values in all the variables as a whole would be removed.
proc sql; select DISTINCT * from outdata; quit;
SAS-defined formats can be used to improve the appearance of the body of a report. You can also label the variables using LABEL keyword.
options label; proc sql; select weight FORMAT= 8.2 , married Label =" Married People" from outdata; Quit;
The ORDER BY clause returns the data in sorted order.
ASC option is used to sort the data in ascending order. It is the default option. DESC option is used to sort the data in descending order.
proc sql; select MoMAge, eight, married from outdata ORDER BY weight ASC, married DESC; Quit;
Use the WHERE clause with any valid SAS expression to subset data.
The BETWEEN-AND operator selects within an inclusive range of values.
Example : where salary between 4500 and 6000;
The CONTAINS or ? operator selects observations by searching for a specified set of characters within the values of a character variable.
Example : where firstname contains 'DE';
OR
where firstname ? 'DE';
The IN operator selects from a list of fixed values.
Example : where state = 'NC' or state = 'TX';
The easier way to write the above statement would be to use the IN operator.
where state IN ('NC','TX');
The IS MISSING or IS NULL operator selects missing values.
Example : where dateofbirth is missing
OR where dateofbirth is null
The LIKE Operator is used to select a pattern.
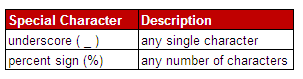
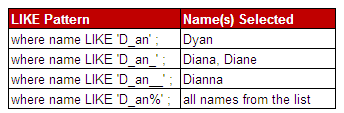
Important Point :
The WHERE clause can reference a previously calculated variable in two ways-
1. Use CALCULATED keyword.
2. Repeat the calculation in the WHERE clause.
Method I :PROC SQL; SELECT momage, (WEIGHT * .01) AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata WHERE CALCULATED NEWWEIGHT > 5; QUIT;Method II :
PROC SQL; SELECT momage, (WEIGHT * .01) AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata WHERE (WEIGHT * .01) > 5; QUIT;
The CASE WHEN statement is used in SQL to perform conditional logic and return different values based on specified conditions. The END statement is required when using the CASE WHEN statement.
PROC SQL; SELECT WEIGHT, CASE WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 0 AND 2000 THEN 'LOW' WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 2001 AND 3000 THEN 'MEDIUM' WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 3001 AND 4000 THEN 'HIGH' ELSE 'VERY HIGH' END AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata; QUIT;
The conditions within the CASE statement are as follows:
- If the weight is between 0 and 2000 (inclusive), it is categorized as 'LOW'.
- If the weight is between 2001 and 3000 (inclusive), it is categorized as 'MEDIUM'.
- If the weight is between 3001 and 4000 (inclusive), it is categorized as 'HIGH'.
- If the weight does not fall into any of the above ranges, it is categorized as 'VERY HIGH'.
The following operators can be used in CASE expression:
- All operators that IF uses (=, <, >, NOT, NE, AND, OR, IN, etc)
- BETWEEN AND
- CONTAINS or '?' (wildcard operator)
- IS NULL or IS MISSING
- = *
- LIKE
Use GROUP BY clause to summarize or aggregate data. Summary functions are used on the SELECT statement to produce summary for each of the analysis variables.
proc sql; select momage, COUNT(married) AS marriage from outdata GROUP BY momage; Quit;
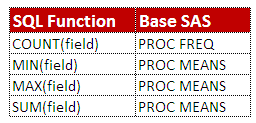
- AVG/MEAN
- COUNT/FREQ/N
- SUM
- MAX
- MIN
- NMISS
- STD
- VAR
- T (t value)
- USS (Uncorrelated Sum of Square)
- CSS (Correlated Sum of Square)
- RANGE
In order to subset data when grouping is in effect, the HAVING clause must be used.The variable specified in having clause must contain summary statistics.
proc sql; select momage, weight, COUNT(married) AS marriage from outdata GROUP BY momage, weight HAVING marriage > 2; Quit;
Important Point -
The WHERE clause cannot be used to subset aggregated data. To subset data with the GROUP BY clause you must use HAVING clause.
The CREATE TABLE statement can be used to create a new data set as output instead of a report produced in output window.
SYNTAX
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE table-name AS SELECT column(s) FROM table(s) | view(s) WHERE expression GROUP BY column(s) ORDER BY column(s); QUIT;
proc sql; create table health AS select weight, married from outdata ORDER BY weight ASC, married DESC; Quit;
Suppose you want to limit the number of rows that PROC SQL produces in the data set, use the INOBS= option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql INOBS=50; create table health AS select weight,married from outdata; Quit;Difference between INOBS= and OUTOBS=
INOBS controls how many records are read from the dataset and OUTOBS controls how many records are written. Run the following program and see the difference. Both returns different results.
/* OUTOBS=Example*/ proc sql outobs=2; select age, count(*) as tot from sashelp.class group by age; quit; /* INOBS= Example */ proc sql inobs=4; select age, count(*) as tot from sashelp.class group by age; quit;
Suppose you are asked to calculate the unique number of age values by Sex columns using SASHELP.CLASS dataset.
You can use PROC SQL with COUNT(DISTINCT variable_name) to determine the number of unique values for a column.
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE TEST1 as SELECT Sex, Count(distinct Age) AS Unique_count FROM sashelp.class GROUP BY Sex; QUIT;
You can use NMISS() function to compute the number of missing values in a variable. The COUNT() function returns the number of non-missing values in a variable.
data temp; input id; cards; 1 2 . 4 5 . ; run;
proc sql; select nmiss(id) as N_missings, count(id) as N, calculated N_missings + calculated N as total from temp; quit;
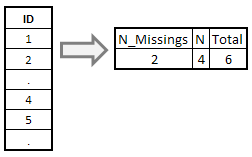
How to refer to a calculated variable
The keyword CALCULATED is used to refer to a newly created variable for further calculation. In this case, we have used CALCULATED to sum 'N_MISSINGS' and 'N' variables.
Suppose you need to keep all the variables from SASHELP.CARS except variables 'MODEL' and 'MAKE'. The DROP= option is used to drop these two variables. Similarly, we can use KEEP= option to keep specific variables. These DROP= and KEEP= Options are not native SQL language. It only works in SAS.
proc sql; create table saslearning (drop= make model) as select * from sashelp.cars; quit;
You can use DELETE FROM statement to remove records (rows) from a dataset.
proc sql; delete from outdata where momage > 0; quit;
In this case, we are deleting all records having momage greater than 0 from outdata dataset. Log shows '478 rows were deleted from outdata'.
Suppose you need to find out employee IDs having records in the table named 'file1' but not in table 'file2'. In the code below, we are querying multiple tables (datasets).
data file1; input ID age; cards; 1 24 2 34 3 45 4 67 ; run; data file2; input ID age; cards; 1 25 3 46 4 62 ; run; Proc SQL; Select ID from file1 Where ID not in (select ID from file2); Quit;
Find employee IDs whose age is in the average age +/- 10 years.
Proc SQL; Select id from file1 where age between (select Avg(age) from file1) - 10 and (select avg(age) from file1)+10; Quit;
In this example, the CASE statement is used to evaluate a condition: whether a student has a score below 70 in any test. To solve this, we have written a subquery that selects "Student_ID" from the "Tests" table where the "Score" is less than 70.
proc sql; select Name,Grade,Teacher, Case When Student_ID in (select Student_ID from Tests where Score lt 70) then 'Failed one or more tests' else 'Passed all tests' end as Test_Results from Students; quit;
If the condition is true, the new column "Test_Results" is assigned the value 'Failed one or more tests.' If the condition is false, the value 'Passed all tests' is assigned to the "Test_Results" column. The result of the query will return the student's name, grade, teacher, and their test results.


Well Done Deepanshu, I was almost new to SQL.
ReplyDeleteBut Now I can say that atleast I have learnt basic steps and statements for PROC SQL.
Could you be so kind to share codes for joints as well.
Check out this article : http://www.listendata.com/2014/06/proc-sql-merging.html
DeleteExcellent information! Thanks.
ReplyDeleteThis is really wonderful.
ReplyDeleteIt is better, let the students try then provide the answers.
VERY NICE AND HELPFUL MATERIAL, HOWEVER I SEE ONE CORRECTION, WHERE CLUASE CAN REFER A COMPUTED VARIABLE USING THE CALCULATED KEYWORD.
ReplyDeletePLEASE CORRECT ME IF MY UNDERSTANDING IS WRONG.
Yes, your understanding is correct. We can use CALCULATED keyword in WHERE clause. Please make a note that the CALCULATED keyword in WHERE clause is not a standard SQL. It’s SAS SQL, which is unique to SAS. Hence i don't recommend to people who are novice to SQL programming.
Deletenice to understand...its very use full for freshers...
ReplyDeletevery nice presentation on sql
ReplyDeleteThank you for writing to me :-)
Deletehow to get SAS
ReplyDeleteCheck out this article - http://www.listendata.com/2014/08/download-and-install-free-version-sas.html
DeleteSincerely admiring ur effort to share knowledge to us. Keep it up sir ji...
ReplyDeleteThank you for your appreciation. Cheers!
Deleteso useful information to have an idea about sql. it also helpful for quick reference toooo.
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it useful.
DeleteI am learning SAS through this. Excellent info for beginners
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for this exposition and explanation. Well done!!!
ReplyDeleteHi Deepanshu could u tell me from where I can get sasuser.outdata dataset
ReplyDeleteoutdata (dataset I mean)
I think you should add screenshots of program and their output
ReplyDeleteI think you should add screenshots of program and their output
ReplyDeleteScreenshot would have been further ease the understanding
ReplyDeleteThanks for your feedback!
DeleteGreat lesson! Thank you so much!
ReplyDeleteproc sql;
ReplyDeleteselect distinct*
from sashelp.class;
quit;
in this code it is not removing duplicate values in the whole dataset.why?
It is because no duplicate record is found in this dataset. If you intend to remove duplicates based on a variable, you can use the code below -
Deleteproc sql;
select distinct age
from sashelp.class;
quit;
Thank you for your post! Very useful and helpful information for a beginner like me.
ReplyDeletehi... i am not getting difference between inobs and outobs even when i am trying both the output is same...plz help...
ReplyDeleteinobs is for no. of obs to fetch from a table while outobs is no. of obs to insert in a table.
DeleteI added explanation with example in the article. Cheers!
DeleteThank you for this great tutorial. Can I practice these Proc SQL statements/code with a regular SAS dataset or do I need to use something else? Thanks!
ReplyDeleteHow i am unable to get SAS data set used in this exercise.. Could you please help me..?
ReplyDeleteDifference between inobs and outobs
ReplyDeleteexample:
Deleteinobs=2; means it will read only two observations from source.
outobs=5; means it will print only 5 observations in output.
while using these two functions we will get a warning alert in log as we are not reading or writing all data to sas.
Its very helpful. Thank you Admin.
ReplyDeleteCan anyone tell..what is more efficient order by or proc sort?
ReplyDeleteCan anyone tell..what is more efficient order by or proc sort?
ReplyDeleteFor a small dataset, there isn’t a big difference in performance between PROC SORT and PROC SQL. However, for larger datasets, PROC SQL is faster than PROC SORT. Also, it seems that sorting character data is easier (read: faster), than numeric data.
DeleteThank you. Great information about SQL. It helps me a lot.
ReplyDeleteSUPER AND VERY VERY GOOD WITH NEAT EXPLANATIONS THANK YOU
ReplyDeleteVery good work and thanks for sharing! However I think there might be one mistake in the article. In point 16, counting unique vallues by a grouping variable, assume we have the following table:
ReplyDeleteCollege_names student_ID score
A 1001 88
A 1002 88
A 1003 88
A 1004 92
B 1005 90
your output would be:
College_names unique_count
A 2 * since there are only 2 distinct scores for A
B 1
But the desired output should be:
College_names score unique_count
A 88 3
A 92 1
B 90 1
Correction:
select college_names, count(student_ID) AS unique_count
from test
group by college_names, score
Correct me if I am wrong.
In 16)Counting unique values by a grouping variable example, how can count(distinct score) give number of students who got same scores?
ReplyDeletegreat job sir.........
ReplyDeleteCan you please share blogs for SAS VA(Visual Analytics) and SAS PM(Predictive Modeling)
ReplyDeletewhere is outdata. articles are very useful but could not get a chance to hands on
ReplyDeleteHi Deepanshu, Can you please provide the outdata, It would be a great help for learning
ReplyDeleteI added outdata dataset in the article. Thanks!
DeleteThis site is really very helpful. A big 👍
ReplyDeleteHi i love this site and article its very helpful.
ReplyDeleteI do have one question How do i solve the problem select the 2nd most highest salary in the dataset for all the customers .is there a way to rank the data.
We can use the rank procedure based on that we can retrieve nth highest salary data.
DeleteWell explained
ReplyDeletecan some one help me..
ReplyDeletedata a;
input party account$ balance;
datalines;
1 A1 50
1 A2 60
1 A3 30
2 A4 40
2 A5 50
3 A6 30
3 A7 90
run;
write a query to fetch all accounts listed to the party who has at least one account having balnce greater than 50?
Hi, The below code will give the result account having balance greater than 50.
Deleteproc sql;
select * from work.a
where balance gt 50;
quit;
Thank you! All I needed was the first image - SFWGHO.
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for sharing information! You are so wonderful!
ReplyDeleteHi sir ... your content on SAS is very very informative and it is explained in very simple way that every beginner can learn it. thanks a lot for providing this platform.. i am SAS learner and learning deeply through your content...
ReplyDeleteGlad you found it useful. Cheers!
Delete