This article explains how to use the INDEX function in SAS, along with examples.
What does the INDEX Function do?
The INDEX function in SAS is used to return the position of the first occurrence of a substring within a character string.
The syntax of the INDEX Function is as follows -
INDEX(string, substring)
- string: The string within which you want to find the substring.
- substring: The substring you want to find within the string.
Let's generate a sample dataset for demonstration purposes.
data mydata; input names $30.; cards; Raj Gates Allen Lee Dave Sandy William Gates Jon Jedi ; run;
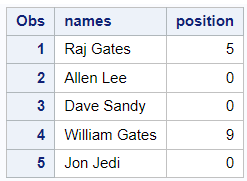
In the example below we are using the INDEX function to find the position of the first occurrence of the string "Gates" in each observation of the variable "names".
data readin; set mydata; position = index(names, "Gates"); proc print; run;
In the above SAS Program, we have created a new variable named position which stores the position of the first occurrence of the string "Gates". The INDEX function returns 0 when the variable does not contain value of "Gates".
How to Handle Case Sensitivity?
The INDEX function is case-sensitive which means it treats "gates", "Gates" and "GATES" as different substrings.
data readin; set mydata; position = index(names, "gates"); proc print; run;
The INDEX function returned 0 because it couldn't find 'gates' in the 'names' variable. 'Gates' does exist in the variable, but the function differentiates between uppercase 'G' and lowercase 'g'.
To fix this issue, we can convert the variable to lowercase using the LOWCASE function. This will result in "Gates" becoming "gates".
data readin; set mydata; position = index(lowcase(names), "gates"); proc print; run;
How to Handle Leading Spaces?
Let's say you have a variable that contains leading spaces. See the sample dataset below. Leading spaces cause a change in the position of a substring within the longer string.
data mydata; input names $char15.; datalines; peter smith peter doe peter johnson ; run;
To fix this, we can use STRIP function to remove leading (and trailing) spaces. Compare the values of two variables named "position" and "position2". The variable "position2" leverages the STRIP function whereas the variable "position" is without the STRIP function.
data readin; set mydata; position = index(names, "peter"); position2 = index(strip(names), "peter"); proc print; run;
How to Filter Data using INDEX Function?
In this example we are using a dataset named CARS from SASHELP library. We want to select only those models that contain "convertible" in their names.
We added a WHERE statement to check if the substring "convertible" exists in the variable. If the result of the INDEX function is greater than 0, it means the substring is found and the record is included in the filtered dataset.
data readin; set sashelp.cars; where index(lowcase(model), 'convertible') > 0; run;





Share Share Tweet