In this post we have covered various ways to handle time and datetime values in SAS, along with examples.
Suppose you have a variable that has a timestamp of 29-Jun-2023 04:59:02.
hour(timestamp)- Extracts hour from timestamp. It returns 4.minute(timestamp)- Extracts minutes from timestamp. It returns 59.second(timestamp)- Extracts seconds from timestamp. It returns 2.timepart(timestamp)- Extracts time from timestamp.datepart(timestamp)- Extracts date from timestamp.put(timepart(timestamp), time8.)- Extracts time from timestamp and formats it. It returns 4:59:02.put(timepart(timestamp), hhmm.)- Extracts time from timestamp and formats it as hours and minutes. It returns 4:59.put(datepart(timestamp),worddate.)- Extracts date from timestamp and formats it in word form. It returns June 29, 2023.put(datepart(timestamp),date11.)- Extracts date from timestamp and formats it. It returns 29-JUN-2023.put(timestamp, dateampm.)- Formats the timestamp as datetime with AM or PM. It returns 29JUN23:04:59:02 AM.put(timestamp, datetime20.)- Formats the timestamp as datetime. It returns 29JUN2023:04:59:02.
In the code below, we are creating a sample SAS dataset for demonstration purposes. This dataset will be used in the examples throughout this tutorial.
data example; input date DATETIME20. sale; datalines; 29-Jun-2023 04:59:02 83 27-Jun-2023 13:51:23 81 run;
How to Extract Time from DateTime
- The
TIMEPARTfunction is used to extract time from datetime values in SAS. - The
HOURfunction is used to extract hour from timestamp in SAS. - The
MINUTEfunction is used to extract minutes from timestamp in SAS. - The
SECONDfunction is used to extract seconds from timestamp in SAS.
In this example, the PUT function is used to convert and format a value into a specific format.
data readin; set example; datetime = put(date, datetime20.); time_hour = hour(date); time_minute = minute(date); time_second = second(date); time8 = put(timepart(date), time8.); hhmm = put(timepart(date), hhmm.); hours52 = put(timepart(date), hour5.2); run;
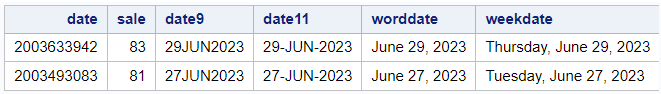
How to Extract Date from DateTime
In SAS, the DATEPART function is used to extract date from datetime values. See the examples below.
data readin; set example; date9 = put(datepart(date),date9.); date11 = put(datepart(date),date11.); worddate = put(datepart(date),worddate.); weekdate = put(datepart(date),WEEKDATE.); run;
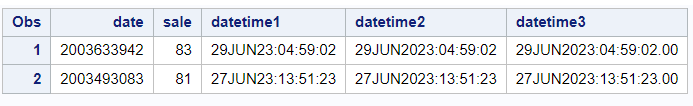
The DATETIMEw.d format shows SAS datetime values in the form ddmmmyy:hh:mm:ss.ss.
The code below creates new variables and assigns them the value of the variable "date" converted to a character using the PUT function. The format is used to specify how the date value should be formatted as a datetime value.
data readin; set example; datetime1= put(date, datetime18.); datetime2= put(date, datetime20.); datetime3= put(date, datetime21.2); run;
The DATEAMPMw.d format displays SAS datetime values in the form ddmmmyy:hh:mm:ss.ss with AM or PM.
data readin; set example; datetime1= put(date, dateampm.); datetime2= put(date, dateampm13.); datetime3= put(date, dateampm22.2); run;




Share Share Tweet