This tutorial explains five different ways to quickly concatenate strings (character values) in SAS.
combined_variable = variable1 || variable2
combined_variable = CAT(variable1, variable2)
combined_variable = CATT(variable1, variable2)
combined_variable = CATS(variable1, variable2)
combined_variable = CATX(delimiter, variable1, variable2)
Let's create a sample dataset for demonstration purpose. This dataset will be used in the examples below.
data have; length first_name $9.; input first_name $ last_name $ sales; cards; Joe Dan 25 Jason Roy 22 Deeps Arora 31 Deepanshu Bhalla 27 ; run;
In SAS, the double vertical bar (||) joins strings. It's the oldest method in SAS to combine strings.
data want; set have; name = first_name || last_name; run;
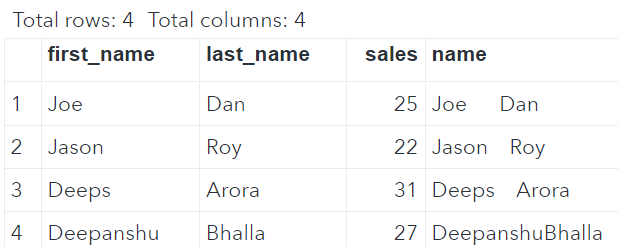
The double vertical bar (||) has a limitation of adding unnecessary spaces when concatenating strings. Refer to the image below. The variable first_name has a length of 9 characters so it adds spaces in all the strings where length is less than 9. It doesn't add a space against name 'Deepanshu' because it has a length of 9 characters. Hence this method is not recommended.
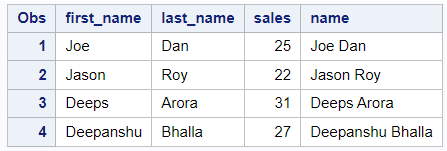
To fix the unnecessary spaces between the text, we can use the STRIP function to remove leading and trailing spaces before concatenating. Here we are adding one space between the first and last name to create a full name.
data want; set have; name = strip(first_name) || " " || strip(last_name); run; proc print data=want; run;
The CAT function combines strings without removing any spaces at the beginning or end. Please note that if any of the variable is numeric, it will be converted to a character string, and any leading or trailing spaces will be removed.
data want; set have; name = cat(first_name, last_name); run;
The CAT Function also has a limitation of having spaces at the end which makes spacing between two strings inconsistent when concatenating the strings.
The CATT function combines strings and removes trailing spaces when concatenating. The extra "T" in "CATT" refers to TRIM function in SAS which removes the trailing blanks.
data want; set have; name = catt(first_name, last_name); run;
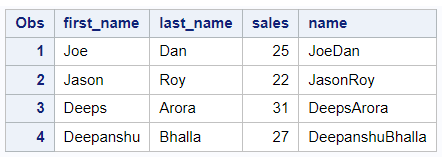
The CATS function combines strings and removes both leading and trailing spaces when concatenating. The "S" in "CATS" refers to the STRIP function which removes both leading and trailing blanks.
data want; set have; name = cats(first_name, last_name); run;
The CATX function combines strings and separates them with a delimiter. The CATX function also removes leading and trailing spaces when concatenating.
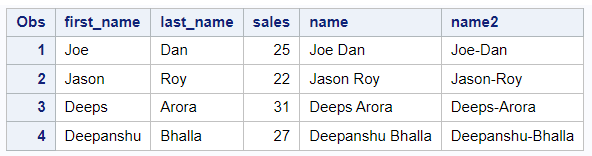
You can specify any delimiter you want in the first argument of CATX function. In the code below, we are showing two different examples wherein we are using one space and "-" as delimiters.
data want;
set have;
name = catx(" ", first_name, last_name);
name2 = catx("-", first_name, last_name);
run;
proc print data=want;
run;
In the table below, we have a comparison of five different methods of concatenation in SAS. It is recommended to use the CATX function.
| Methods | Removes spaces (Character) | Removes spaces (Numeric) | Delimiter |
|---|---|---|---|
| || | No | No | No |
| CAT Function | No | Yes | No |
| CATT Function | Trailing | Yes | No |
| CATS Function | Leading and Trailing | Yes | No |
| CATX Function | Leading and Trailing | Yes | Yes |


Share Share Tweet