SAS Arrays : Introduction
SAS arrays provides a simple, efficient way to process a list of variables in a SAS DATA step. In other words, arrays are useful when you need to perform similar operations on multiple variables or when you want to avoid writing similar code for multiple variables.
Syntax of SAS Arrays
The syntax of SAS arrays is as follows:
Array array-name {number-of-elements} list-of-variables;
Note: You can use [ ] or { } or ( ) for defining number of elements in the ARRAY statement.
ARRAY ABC[5] a b c d e;: ABC is an array-name, 5 implies the number of variables in the array, and "a b c d e" are the fields that make up the array.ARRAY ABC[*] a b c d e;: In this example, SAS would automatically calculate the number of variables in the array.ARRAY ABC[*] X1-X10;: Where the X1 variable contains the X1 value, X2 contains the X2 value, etc.ARRAY ABC[*] $ X1-X10;: If the variables are of character type then use $ sign before specifying list of variables.
SAS DO Loop : Introduction
The DO loop allows you to perform iterative processing. You can use the DO loop to repeat a set of statements for a specific number of iterations or for a particular range of values.
Syntax of SAS DO Loop
The syntax of SAS DO Loop is as follows:
DO index-variable = start-value TO end-value; /* Statements to be executed inside the loop */ END;
- index-variable: This is a temporary variable used to keep track of the loop iterations. It is usually a numeric variable.
- start-value: This is the initial value for the index variable.
- end-value: This is the final value for the index variable.
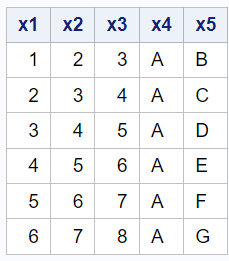
Let's create a sample SAS dataset for demonstration purposes.
 |
| SAS Array : Example |
data temp; input x1 x2 x3 x4$ x5$; cards; 1 2 3 AA BB 2 3 4 AB CC 3 4 5 AC DD 4 5 6 AD EE 5 6 7 AE FF 6 7 8 AF GG ; run;
The following code reads data from the "temp" dataset and then goes through each observation and checks if the values of the variables "x1," "x2," and "x3" are greater than 3. If any of these values are greater than 3, the value is replaced with a missing value. It stores the updated values in a new dataset "test".
data test;
set temp;
array nvars {3} x1-x3;
do i = 1 to 3;
if nvars{i} > 3 then nvars{i} =.;
end;
run;
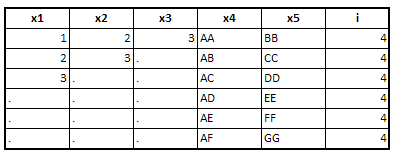 |
| Output : Array Statement |
The first time the loop processes, the value of "i" is 1; the second time, 2; and the third time, 3. At the beginning of the fourth iteration, the value of "i" is 4, which is found to be greater than the stop value of 3 so the loop stops. The value of i is now 4 and not 3, the last value before it would be greater than 3 as the stop value.
Note : We can drop variable "i" with drop statement or drop data set option.Efficient version of the above code
data test;
set temp;
array nvars (*) _numeric_;
do i = 1 to dim(nvars);
if nvars{i} > 3 then nvars{i} =.;
end;
drop i;
run;
Notes -
- The "_numeric_" is used to specify all the numeric variables.
- The DIM function returns the number of elements (variables).
The following code reads data from the "temp" dataset and then goes through each character variable and keeps only the first letter, discarding the rest. The result is a new dataset "test" with character variables truncated to their first letters.
data test;
set temp;
array cvars (*) _character_;
do i = 1 to dim(cvars);
cvars{i} = substr(cvars{i},1,1);
end;
drop i;
run;
Note - The "_character_" is used to specify all the character variables.
The following code reads data from the "temp" dataset and then goes through each character variable and extracts the first letter from each variable, and assigns it to the corresponding "X6" or "X7" variable in the "test" dataset. The result is a new dataset "test" with the first letter of each character variable stored in "X6" and "X7" variables.
data test;
set temp;
array cvars (*) _character_;
array dvars (*) $ X6 X7;
do i = 1 to dim(cvars);
dvars{i} = substr(cvars{i},1,1) ;
end;
drop i;
run;
The following code reads data from the "temp" dataset and then goes through each numeric variable in "temp" and multiplies it by a corresponding percentage increase factor from the temporary "pctinc" array. The results are assigned to the "px1", "px2", and "px3" variables in the "abcd" dataset. The temporary array "pctinc" is used for the calculation but is not included in the final dataset.
data abcd;
set temp;
array nvars (*) _numeric_;
array pvars (*) px1 px2 px3;
array pctinc {3} _temporary_ (1.1 , 1.2 ,1.3);
do i = 1 to dim(nvars);
pvars{i} = nvars{i} * pctinc{i};
end;
drop i;
run;
Notes -
- In the above example, we are multiplying values of variables with different numbers.
- When the key word _TEMPORARY_ is used in a ARRAY statement, data elements are created but are not stored in the data file.
The following code reads data from the "temp" dataset and then calculates the difference and percentage difference between consecutive numeric variables in "temp" and stores the results in the temporary "diff" and "percent" arrays. The final "abcd" dataset will not include the temporary "diff" array but will have the percentage differences stored in the "percent" array.
data abcd;
set temp;
array nvars(*) _numeric_;
array diff{2} _temporary_;
array percent{2};
do i = 1 to 2;
diff{i} = nvars{i +1} - nvars{i};
percent{i} = diff{i} / nvars{i} ;
end;
drop i;
run;
Using the OF Operator in a SAS Array
The following two codes are equivalent :
array gnp (*) x y z; sumgnp = sum(of gnp(*));OR
sumgnp = sum(x,y,z);
Calculate the mean : mean_score = mean(of gnp(*));
Calculate the minimum : min_score = min(of gnp(*));
Suppose you are asked to create a flag in cases wherein sum of variables x1,x2 and x3 is greater than 10.
data test; set temp; array nvars (*) x1-x3; if sum(of nvars(*)) > 10 then flag =1; else flag=0; run;
The DO OVER loop is one of the most useful DO loops. It can be used with an array when indexing of the array is not needed.
In the example below, the "do over" statement iterates over each numeric variable in the array "nvars". For each variable, the code checks if its value is greater than 3. If it is, then the value is set to missing (represented by a dot "."). This effectively replaces any numeric value greater than 3 with a missing value.
data test; set temp; array nvars _numeric_; do over nvars; if nvars > 3 then nvars = .; end; run;




its very useful and easily understandable for starters like me ... thank you ...keep posting
ReplyDeleteIt is really good and understandable. Really helpful for the people who are trying to come in SAS. Keep Posting..... Thanks:)
ReplyDeletegood content but confusing without actual figures to imagine the process
ReplyDeleteThe content is very good. Please keep it up.
ReplyDeleteThanks for your teaching. Its easy to understand. Much appreciated
ReplyDeleteThe examples are easy to understand thanks a lot for posting but I didn't understand what is the use of 1,1 in this example
ReplyDeletedata test;
set temp;
array cvars (*) _character_;
array dvars (*) $ x6 X7;
do i = 1 to dim(cvars);
dvars{i} = substr(cvars{i},1,1) ;
end;
drop i;
run;
Substring starting character 1 and length is 1
ReplyDeleteNice site--you showed me some PROC FREQ options that I wasn't aware of!
ReplyDeleteNOTE: If there are more than 2 character variables you'll get an error here because it will try to reference an index that doesn't exist in the second array with only 2 members.
data test;
set temp;
array cvars (*) _character_;
array dvars (*) $ x6 X7;
do i = 1 to dim(cvars);
dvars{i} = substr(cvars{i},1,1) ;
end;
drop i;
run;
can anyone explain do over loop in detail. .what is mean by indexing of array ??
ReplyDeleteIndexing here means that we do not need to declare any variables as we did it in first code. If the operation needs to be performed on all the variables then you do not need to define any array with an index it will automatically pick all the variables and work on it.
DeleteI have to multiply 1 column(n observation) to single value .what would be syntax?
ReplyDeleteCan someone answer....1). which function is used to count variables /values in sas?
ReplyDeletehow do you flag when a variable is greater than a specific length in array
ReplyDeleteExcellent tutorial. Thank you very much for sharing your knowledge in such easy to understand way.
ReplyDeleteData sales;
ReplyDeleteDo year=1 to5;
Do month=1 to 12;
X+1;
Output;
End;
End;
Run;
Sales data contain number of records?
Could you please solve this question
i want
ReplyDeletedo i=1 to 12;
it gives 1 up to 12 but i want jan to dec plz i needed
any one helpme
add format to the month variable
DeleteVery helpful content.. Thanks
ReplyDeleteThank you. Very helpful information with understandable example and notes.
ReplyDeleteData ex1;
ReplyDeleteDo i=1 to 10;
End;
Run;
Data ex2;
Do i=1 to 10;
Output;
End;
Run;
Data ex3;
Do i=1 to 10;
Output;
End;
Output;
Run;
In those we getting different output why,how inner process happens, please explain
awesome! good examples to nail home the basics. hard to find simple examples that makes sens.
ReplyDelete