The purpose of this post is to help you understand the difference between linear regression and logistic regression. These regression techniques are two most popular statistical techniques that are generally used practically in various domains. Since these techniques are taught in universities, their usage level is very high in predictive modeling world. In this article, we have listed down 13 differences between these two algorithms.
Difference between Linear and Logistic Regression
1. Variable Type : Linear regression requires the dependent variable to be continuous i.e. numeric values (no categories or groups).
While Binary logistic regression requires the dependent variable to be binary - two categories only (0/1). Multinominal or ordinary logistic regression can have dependent variable with more than two categories.
Difference between Linear and Logistic Regression
1. Variable Type : Linear regression requires the dependent variable to be continuous i.e. numeric values (no categories or groups).
While Binary logistic regression requires the dependent variable to be binary - two categories only (0/1). Multinominal or ordinary logistic regression can have dependent variable with more than two categories.
2. Algorithm : Linear regression is based on least square estimation which says regression coefficients should be chosen in such a way that it minimizes the sum of the squared distances of each observed response to its fitted value.
While logistic regression is based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation which says coefficients should be chosen in such a way that it maximizes the Probability of Y given X (likelihood). With ML, the computer uses different "iterations" in which it tries different solutions until it gets the maximum likelihood estimates.
While logistic regression is based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation which says coefficients should be chosen in such a way that it maximizes the Probability of Y given X (likelihood). With ML, the computer uses different "iterations" in which it tries different solutions until it gets the maximum likelihood estimates.
3. Equation :
Multiple Regression Equation :
Multiple Regression Equation :
Y is target or dependent variable, b0 is intercept. x1,x2,x3...xk are predictors or independent variables. b1,b2,b3....bk is coefficients of respective predictors.
Logistic Regression Equation :
P(y=1) = e(b0 + b1x1 + b2x2 +-----bkxk) / (1+e(b0+b1x1+ b2x2+------bkxk))
Which further simplifies to :
P(y=1) = 1 / (1+ exp -(b0+b1x1+ b2x2+------bkxk))
 |
| Logistic Regression Equation |
The above function is called logistic or sigmoid function.
4. Curve :
Linear Regression : Straight line
 |
| Straight Line : Linear Regression |
Linear regression aims at finding the best-fitting straight line which is also called a regression line. In the above figure, the red diagonal line is the best-fitting straight line and consists of the predicted score on Y for each possible value of X. The distance between the points to the regression line represent the errors.
Logistic Regression : S Curve
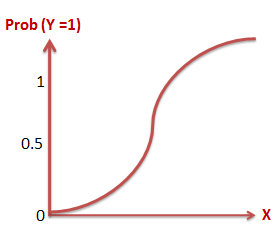 |
| Logistic S-shaped curve |
5. Linear Relationship : Linear regression needs a linear relationship between the dependent and independent variables. While logistic regression does not need a linear relationship between the dependent and independent variables.
6. Normality of Residual : Linear regression requires error term should be normally distributed. While logistic regression does not require error term should be normally distributed.
7. Homoscedasticity : Linear regression assumes that residuals are approximately equal for all predicted dependent variable values. While Logistic regression does not need residuals to be equal for each level of the predicted dependent variable values.
8. Sample Size : Linear regression requires 5 cases per independent variable in the analysis.While logistic regression needs at least 10 events per independent variable.
9. Purpose : Linear regression is used to estimate the dependent variable incase of a change in independent variables. For example, relationship between number of hours studied and your grades.
Whereas logistic regression is used to calculate the probability of an event. For example, an event can be whether customer will attrite or not in next 6 months.
10. Interpretation : Betas or Coefficients of linear regression is interpreted like below -
Keeping all other independent variables constant, how much the dependent variable is expected to increase/decrease with an unit increase in the independent variable.
In logistic regression, we interpret odd ratios -
The effect of a one unit of change in X in the predicted odds ratio with the other variables in the model held constant.11. Distribution :
Linear regression assumes normal or gaussian distribution of dependent variable. Whereas, Logistic regression assumes binomial distribution of dependent variable. Note : Gaussian is the same as the normal distribution. See the implementation in R below -
R Code :
Create sample data by running the following script
set.seed(123)Linear Regression
y = ifelse(runif(100) < 0.5, 1,0)
x = sample(1:100,100)
y1 = sample(100:1000,100, replace=T)
glm(y1 ~ x, family = gaussian(link = "identity"))
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
600.6152 -0.8631
Degrees of Freedom: 99 Total (i.e. Null); 98 Residual
Null Deviance: 7339000
Residual Deviance: 7277000 AIC: 1409
glm(y ~ x, family = binomial(link = "logit"))Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-0.024018 0.005279
Degrees of Freedom: 99 Total (i.e. Null); 98 Residual
Null Deviance: 137.2
Residual Deviance: 136.6 AIC: 140.6
Linear regression uses Identity link function of gaussian family. Whereas, logistic regression uses Logit function of Binomial family.
13. Computational Time: Linear regression is very fast as compared to logistic regression as logistic regression is an iterative process of maximum likelihood.



good explanation
ReplyDeletevery helpfull. i made my assignment easily
ReplyDeletethanks
good
ReplyDeleteits very helful for me doing my assignment but i need 8 more differences and 3 similarities. by the way thankx
ReplyDeleteI have expanded the list of difference between these two algorithms. Thanks!
DeleteI love the way you explain things. Your site has helped me immensely! I can't thank you enough! Keep up the good work!
ReplyDeleteA helpful post. Tks you very much! I have a data with over 48000 observes and category outcome (0 and 1). https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B0viyEhVYPseQlJ5d2pZa3RKc0E/view?usp=sharingBad rate = 80%. I run 2 model for that data: linear and logistics regression. I want to know which model is better? So I have a question: Which common criterions do compare good level of them? In linear model, we have R-squared. Similarity, we have GINI index, -2Loglikehood,sensitivity,specificity,area under ROC curve,... in logistics regression. But have not common criterions to evaluate good level of 2 model. Can you help me? If you can, please give me SAS code for it.
ReplyDeleteA helpful post. Tks you very much! I have a data with over 48000 observes and category outcome (0 and 1). Here is a link to my data: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B0viyEhVYPseQlJ5d2pZa3RKc0E/view?usp=sharing . I run 2 model for that data: linear and logistics regression. I want to know which model is better? So I have a question: Which common criterions do compare good level of them? In linear model, we have R-squared. Similarity, we have GINI index, -2Loglikehood,sensitivity,specificity,area under ROC curve,... in logistics regression. But have not common criterions to evaluate good level of 2 model. Can you help me? If you can, please give me SAS code for it. Thank you!
ReplyDeletevery helpful
ReplyDeleteIf the independent variable is discrete but continuous...wat technique we can use?
ReplyDeleteCorrection: dependent variable
DeleteDependent variable can not be discrete and continous at the same time. It can be onlt any one at a time. As pointed in article, for continuous variable, you can use linear regression. For discrete variable, you can make categories out of them and then use normal logistic regression.
DeleteCan anyone explain in detail about odds ratio?
ReplyDeleteThanks in advance
An excellent explanation. Very useful indeed Thanks
ReplyDeleteClear & crisp 👍
ReplyDeleteExcellent Comparison.
ReplyDeleteSuperb explanations about both terms.
ReplyDeleteExcellent
Very nicely explained
ReplyDeleteVery relevant article***
ReplyDeleteVery nice explanation
ReplyDeleteNICE ARTICLE
ReplyDeleteCan you add a reference to support the minimum sample size of 5 for the linear regression, or explain why did you chose 5?
ReplyDeleteGood explanation very helpful to understand difference between both algorithm
ReplyDelete