In R, you can extract character columns from a data frame using various methods.
Let's create a sample data frame called mydata having 3 variables (name, city, age).
# Create a sample data frame
mydata <- data.frame(
name = c("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"),
city = c("Los Angeles", "New York", "Dallas"),
height = c(165.5, 180.0, 172.3)
)
How to Extract ALL Character Variables in R
In the dataframe named "mydata", we have two character columns "name" and "city". When we have multiple variables in a dataframe, we don't know the name of the character columns in advance.
Base R
character_columns <- mydata[sapply(mydata, is.character)] print(character_columns)
In base R, you can extract multiple character columns using sapply function. The sapply function is a part of apply family of functions. They perform multiple iterations (loops) in R.
In dplyr package, the select_if function is used to select columns based on a condition. In this case, is.character selects only the character columns.
dplyr
library(dplyr) # Select character columns using select_if() character_columns <- mydata %>% select_if(is.character) print(character_columns)
Extract Character Variables with more than 2 Unique Categories in R
Let's modify the "mydata" dataframe by adding one more character variable for demonstration purpose.
mydata <- data.frame(
name = c("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "Jon"),
product = c("A", "A", "A", "B"),
sales = c(21, 32, 45, 36)
)
Base R
In this code, we're using the sapply function to iterate through each column of the "mydata" data frame. For each column, we check if it's of character data type (is.character(col)) and if it has more than 2 unique categories (length(unique(col)) > 2).
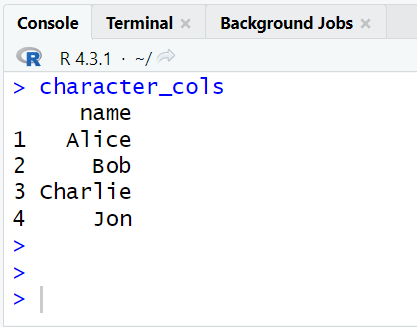
# Extract character columns with more than 2 unique categories character_cols0 <- sapply(mydata, function(col) is.character(col) && length(unique(col)) > 2) # Select columns based on the extracted character column indicators character_cols <- mydata[character_cols0] print(character_cols)
dplyr
In this code, we are using the select_if function from dplyr package which is used to select columns based on a condition. In this case, we are selecting columns that are of character data type (is.character(col)) and have more than 2 unique categories (length(unique(col)) > 2).
library(dplyr) character_cols <- mydata %>% select_if(function(col) is.character(col) && length(unique(col)) > 2) print(character_cols)
Extracting Character Variables with No Missing Values in R
Let's say you want to keep character variables that have no missing values in R.
# Create a sample data frame
mydata <- data.frame(
name = c("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "Jon"),
city = c("Los Angeles", "New York", "Dallas", NA),
height = c(165.5, 180.0, 172.3, 181)
)
Base R
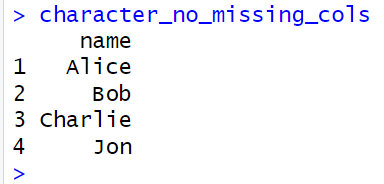
character_cols <- sapply(mydata, is.character) character_no_missing <- colSums(is.na(mydata[character_cols])) == 0 character_no_missing_cols <- mydata[character_cols] [character_no_missing]
Let's see how this code works:
sapply(mydata, is.character)checks and returns if each column in mydata is character type.colSums(is.na(mydata[character_cols])) == 0identifies character columns with no missing values.mydata[character_cols][character_no_missing]selects character columns without missing values and is stored into a new dataframe.
dplyr
If you want to keep columns that have no missing values, you can use the select() function with where() in dplyr. select(where(is.character)) selects only the character columns. select(where(~ all(!is.na(.)))) selects columns where all values are not missing (NA).
library(dplyr) character_no_missing_cols <- mydata %>% select(where(is.character)) %>% select(where(~ all(!is.na(.))))



Share Share Tweet